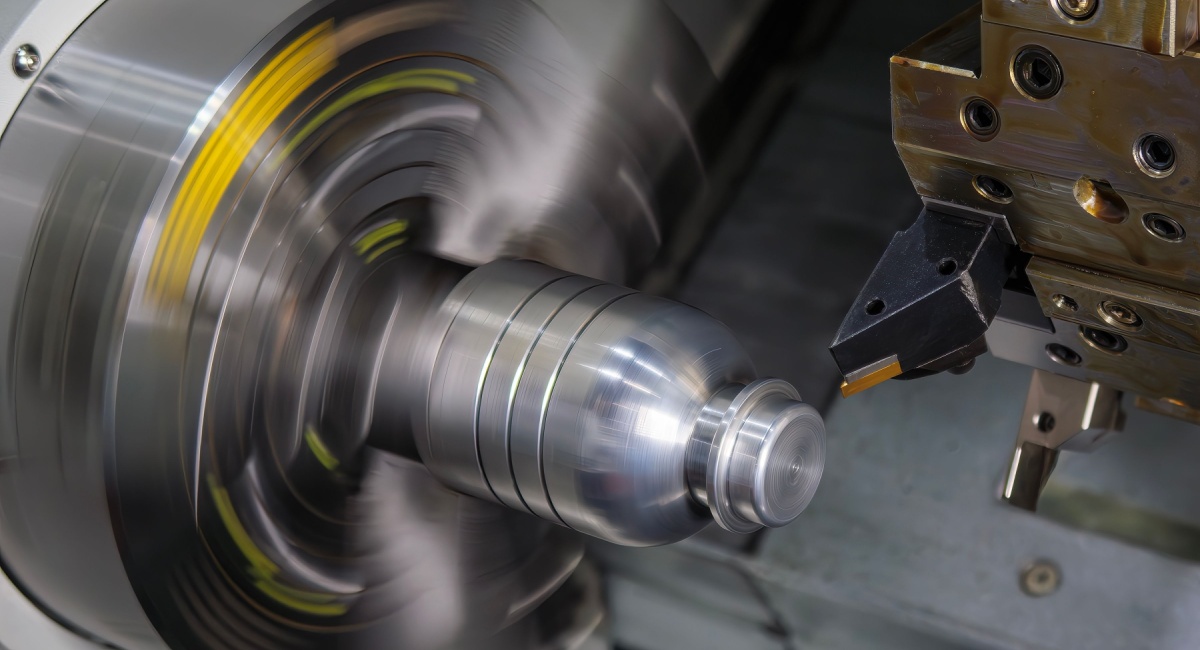
CNC Turning in Manchester, NH, refers to a precision machining process for manufacturing cylindrical and rotational components with controlled geometry. CNC turning is used at Roberson Machine Company to support parts that repeat cleanly across production runs and future releases.
Learn more about:
- How CNC turning supports production-scale components
- How CNC turning pairs with multi-axis machining processes
- Industries and applications that depend on turned features
- How to move forward with a CNC turning project
CNC turning is used across medical, aerospace, automotive, automation, and industrial equipment manufacturing to produce high-volume cylindrical components as well as parts that combine turning, drilling, and milled features in a single workflow—including many everyday machinery components produced at scale. We support short-, medium-, and long-run CNC turning programs across a broad mix of materials and part geometries. To talk through your Manchester, NH, CNC Turning project, contact us online or call 573-646-3996.
Table of Contents
- What CNC Turning Does Best in Production
- Industries That Rely on CNC Turning
- When CNC Turning Is the Right Method for Part Production
- CNC Turning & Precision Machining Capabilities
- Frequently Asked Questions | CNC Turning
- Why Choose Roberson Machine Company for CNC Turning in Manchester, NH?
For more insight into Manchester, NH, CNC turning, materials, and production workflows, explore our case studies, blog, FAQs, and customer reviews. These resources illustrate how turned features and multi-axis machining come together across real-world applications.
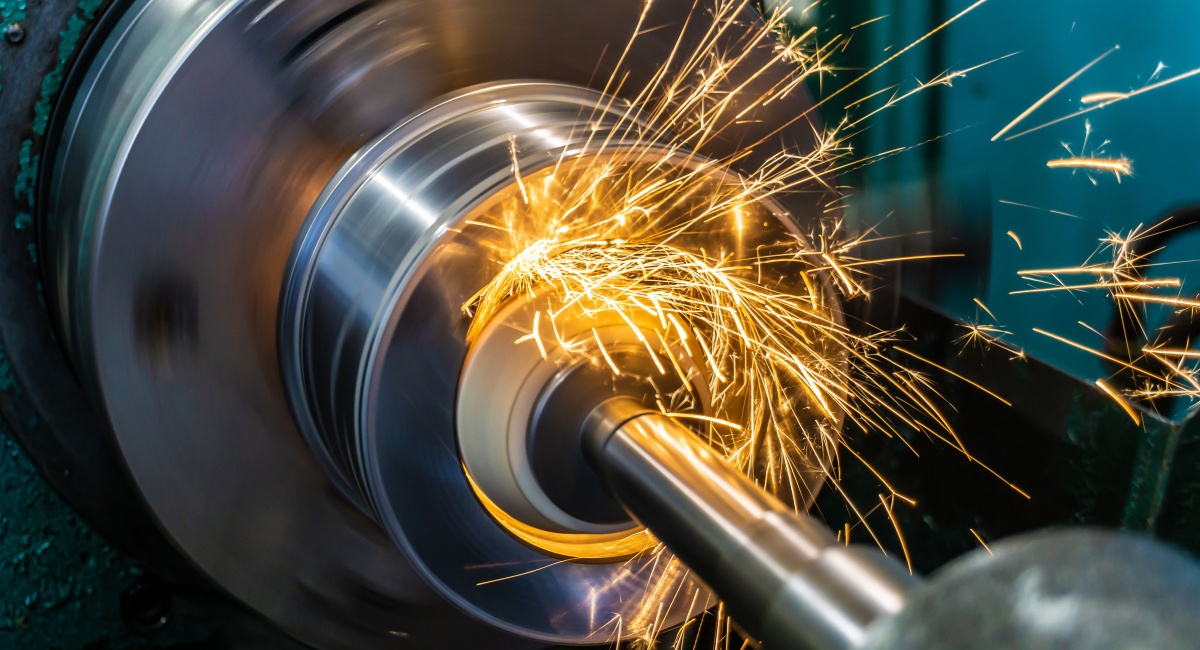

What CNC Turning in Manchester, NH, Does Best in Production
CNC turning occupies a specific place in modern manufacturing by producing accurate, repeatable geometry on parts where round features, concentric relationships, and surface control drive performance. In production environments, turning creates the diameters, bores, threads, and functional surfaces that subsequent operations depend on—commonly within broader contract manufacturing workflows.
When applied correctly, CNC turning supports stable workflows across short runs, high-volume production, and repeat releases. At Roberson Machine Company, our role is to help scale output without introducing variation—using turning as the foundation that supports downstream milling, assembly, inspection, and quality control.
Establishing Critical Diameters & Concentric Geometry
CNC turning plays a key role in establishing the core geometry that governs how a part functions. Because diameters, bores, shoulders, threads, and sealing surfaces are created from a single rotational centerline, turning operations can better control concentric geometry and reduce runout.
This approach is particularly important for parts and assemblies where geometry must remain aligned throughout production and use, including:
- Rotational features that must maintain alignment during assembly
- Interfaces shared with bearings, seals, and mating components
- Parts that are built around consistent centerlines across operations
By anchoring features along a shared axis, Manchester, NH, CNC turning experts reduce stack-up errors while keeping critical relationships aligned. This foundation allows downstream milling, cross-drilling, and secondary operations to add features without compromising fit or function.
Achieving Repeatability Across Volume & Release Cycles
In production machining work, repeatability, not accuracy alone, is what carries a successful first run into a dependable process. CNC turning supports repeatability by keeping key variables controlled and consistent from part to part, an advantage that becomes critical when moving from initial runs into mass production.
Holding geometry to a consistent rotational centerline
By establishing critical features from a shared axis, CNC turning helps ensure diameters, bores, threads, and sealing surfaces remain aligned across every part in a run. This is critical in real-world applications where components need to interface cleanly with bearings, seals, housings, or rotating assemblies—especially when transitioning from prototype quantities into production volume.
Using stable workholding and repeatable setups
Consistent fixturing and workholding reduce variation between parts and between runs. When setups remain unchanged across releases, CNC turning can maintain dimensional stability even as production scales or schedules shift.
Applying the same tool paths, offsets, and cutting conditions
Repeatable programs and controlled cutting parameters help control variation introduced by operator changes, setup drift, or gradual process changes as production scales. Issues such as machine drift can compound across long runs if programs, offsets, or setups aren’t consistently maintained.
When repeatability is built into the process, manufacturers can plan production with confidence and avoid rework when parts are released again months—or years—later. When Manchester, NH, CNC turning is applied with a production mindset, it provides a reliable foundation for scaling output—whether parts are produced internally or as part of a broader contract manufacturing strategy.
Efficient Production of Cylindrical and Rotational Parts
CNC turning is well suited for efficiently producing round and rotational parts. When diameters, bores, threads, and axial features define how a part functions, turning removes material in a continuous, controlled motion that minimizes cycle time, non-cutting time, and unnecessary tool movement.
When production environments involve repeating parts, bar-fed stock, single-axis rotation, and one-setup machining allow CNC turning to preserve consistent geometry while limiting handling and re-clamping. These advantages map closely to production-driven CNC methods built around throughput and process stability.
- Shafts, pins, and rotational hardware that transfer motion and must maintain consistent diameters across long runs.
- Bushings, sleeves, and wear components that rely on alignment and surface finish for service life and proper fit.
- Rollers and cylindrical tooling found in continuous-duty equipment that cycles and follows scheduled replacement.
- Turn–mill hybrid parts that combine rotational geometry and milled features within a single setup.
For parts of this type, Manchester, NH, CNC turning brings together the speed, accuracy, and process control required to support short runs and long-term manufacturing programs.

Industries in Manchester, NH, That Rely on CNC Turning
CNC turning plays a key role across industries in industries where controlled surface finishes and rotational geometry, paired with concentric features, drive performance, reliability, and service expectations.
Medical & Regulated Manufacturing
Across medical machining and manufacturing, CNC turning commonly produces the features that seal, align, or interface with other components. Minor variation in diameters, bores, or surface finishes can affect fit, function, or inspection results.
CNC-turned components are used in precision valve bodies, microscope and alignment assemblies, precision housings, and small-scale medical instrument parts where concentric geometry and surface control outweigh raw material removal speed.
Automotive production machining and EV manufacturing use CNC turning to support high-volume components where diameters, threads, and concentric relationships must hold across thousands—or millions—of parts.
- Processes that must maintain stability as production volume increases
- Features that interface repeatedly with bearings, seals, and mating parts
- Geometry that must not drift between early releases and long-term production
In production work involving drive shaft components, this reality shows up when dimensional control must be maintained across extended runs and small geometric shifts ripple into assembly and performance issues.
Industrial Automation, Robotics & Production Equipment
Throughout industrial automation and robotics, turned components are expected to cycle continuously, align precisely, and wear predictably. CNC turning supports bushings, guides, rollers, and hybrid turn–mill parts used in automated systems where downtime is costly and replacement parts are expected to drop in without adjustment.
This is particularly true for assemblies such as end-of-arm robotic tooling, where concentric geometry, mounting alignment, and repeatability have a direct impact on positioning accuracy and cycle performance.
Aerospace & Defense
Strict performance and verification standards govern aerospace machining and defense manufacturing, where CNC turning supports components with zero tolerance for geometric drift or process variation.
- Load & mechanical stress: Turned features are expected to maintain alignment and dimensional stability under sustained and cyclic loads.
- Vibration & dynamic forces: Rotational components are required to resist runout and surface degradation that contribute to vibration during operation.
- Long service cycles: Geometry and finishes must remain consistent over long service cycles where wear, fatigue, and thermal exposure accumulate.
- Process control & traceability: Turning operations are required to repeat cleanly across validated releases and documented production runs.
Manchester, NH, CNC turning provides the level of control and process stability required to meet these constraints over long service lives.
Energy, Oil & Gas
Within energy and oil & gas machining environments, turned components are subjected to pressure, heat, wear, and corrosive service conditions. CNC turning supports parts where geometry, material behavior, and surface integrity are critical to service life.
- Pressure and fluid containment: Across repeated pressure cycles, turned valve components and manifolds must hold concentric alignment and sealing performance—key considerations in what matters most in oil & gas CNC machining.
- Wear, heat, and material stress: When geometry drifts or finishes degrade, continuous exposure accelerates failure, which is why precision machining plays a role in reducing waste across long production cycles.
- Surface durability: Long-term service performance frequently depends on post-machining decisions such as surface treatments that improve resistance to corrosion, abrasion, and harsh operating conditions.
CNC turning provides the process control needed to meet these demands without introducing variability across long production runs—especially in environments where heat, pressure, and material behavior introduce additional operational and safety considerations.
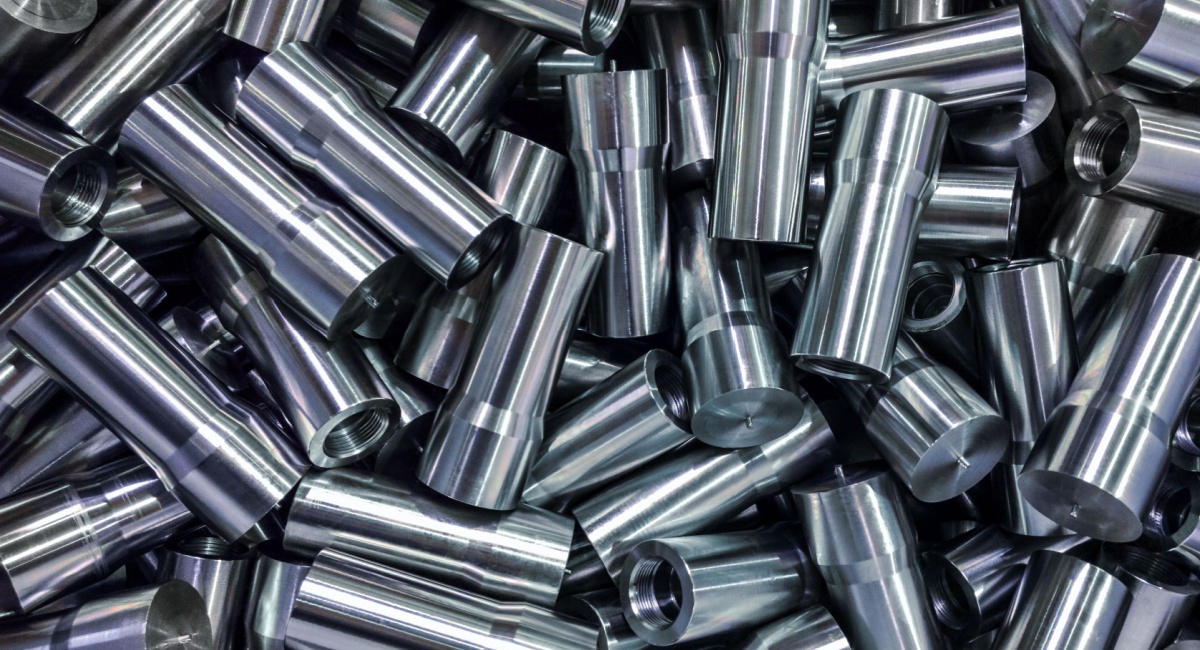

When CNC Turning Is the Right Method for Part Production
CNC turning in Manchester, NH, is a strong fit when a part’s function depends on rotational accuracy, concentric relationships, and controlled surface finishes.
From bushings and pins to rollers and turn–mill tooling equipment, turned parts tend to require:
- Rotational geometry, diameters, bores, or axial features that define how components align, seal, or rotate.
- Features required to remain concentric to a shared centerline through multiple operations, assemblies, or service cycles.
- Surface finishes that determine how parts interface with bearings, seals, fluids, or wear surfaces.
- Geometry that must repeat reliably from first article through long production runs and future releases.
- Multiple features best completed in a single setup to maintain alignment between turned and milled elements.
Production Use Cases for CNC Turning
These requirements appear consistently across different production environments. Common CNC turning parts include:
- Sealing, flow, and pressure-handling parts: Precision valve bodies, fluid-handling components, and other turned features used where sealing performance matters.
- Alignment-critical components: Bushings, sleeves, housings, microscope parts, and sensor mounts where clean alignment during assembly is required.
- Motion-transfer and drive components: Shafts, pins, and rotary hardware produced at volume, including drive shaft components.
- Continuous-duty rollers and cylindrical tooling: High-cycle rollers and guides like ink rollers used throughout production and packaging equipment.
Turned parts rarely exist in isolation within production workflows. Rotational features are commonly combined with milled flats, slots, or mounting interfaces, which makes CNC turning a foundational step in broader, multi-operation machining workflows.
CNC Turning & Precision Machining Capabilities
Many turned parts require additional machining operations to finish functional features, preserve alignment, or limit downstream handling. At Roberson Machine Company, CNC turning runs within a broader workflow that emphasizes repeatability and release consistency.
Based on how the part is designed, Manchester, NH, CNC turning often draws on a range of CNC machining capabilities:
- CNC Milling — Non-rotational features like flats, pockets, and slots finished after turning.
- Precision CNC Machining — For secondary features, dimensional refinement, and finishing after turning.
- Multi-Axis CNC Machining — That keeps cross-holes and angled features aligned without added setups.
- 5-Axis CNC Machining — Applied when parts need access from multiple orientations within one workflow.
- Wire EDM — For machining hardened materials or internal profiles that conventional methods can’t handle.
- Prototyping & First-Article Production — To validate designs before repeat or long-term production.
In Manchester, NH, CNC turning workflows with multiple operations share a simple goal: Complete the part efficiently, maintain alignment between features, and avoid unnecessary handoffs.
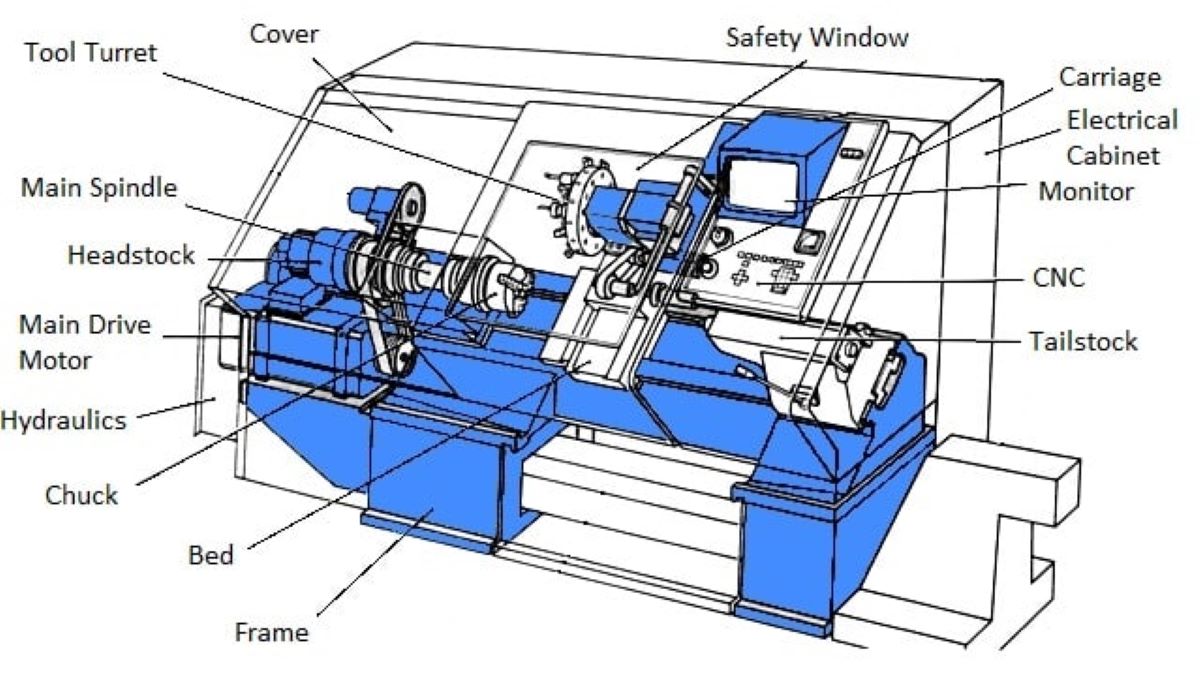
Lathe Machines vs. Turning Centers
While CNC lathes and CNC turning centers both perform turning operations, they are used differently across production environments. This distinction isn’t about how the machines look or how old they are, but about capability, automation, and single-setup efficiency.
CNC Lathes
Operate on two primary axes (X and Z) and are well suited for basic turning work. Traditional CNC lathe machining is often chosen when parts require consistent diameters, faces, grooves, or threads without significant secondary operations.
CNC Turning Centers
By incorporating live tooling, additional axes, sub-spindles, and automation, turning centers support more complex work than basic lathes. CNC turning centers perform drilling, tapping, milling, and back-working in one setup to minimize handoffs and maintain feature alignment.
The right choice depends less on machine complexity and more on how efficiently a part can be completed from start to finish—an important consideration when choosing a CNC turning partner in Manchester, NH, for production work.
Frequently Asked Questions | Part Production & CNC Turning in Manchester, NH
When CNC turning is evaluated for production, the key considerations are typically fit, scale, and long-term consistency. These FAQs address how turning supports real-world production requirements.
In what situations is Manchester, NH, CNC turning the right fit for production parts?
CNC turning is typically the right choice when a part’s function depends on rotational accuracy, consistent diameters, or features that must stay aligned to a common centerline.
CNC turning is especially effective for parts that repeat at volume, need controlled surface finishes, or support additional machining operations.
What kinds of components are well suited for CNC turning?
Production CNC turning in Manchester, NH, is commonly used for parts like:
- Shafts, pins, and rotational hardware
- Bushings, sleeves, and wear components
- Valve bodies, manifolds, and flow-control parts
- Rollers and cylindrical tooling for automated equipment
- Turn–mill components that combine rotational and milled features
These components often play key alignment, sealing, or motion-transfer roles within larger assemblies.
What details help generate an accurate CNC turning quote?
The clearest quotes come from understanding how the part will be produced and released over time. Helpful inputs include:
- Current drawings with tolerances and critical feature callouts
- Material specifications and finish requirements
- Expected quantities per release and annual volume
- Delivery cadence or production schedule
- Inspection, documentation, or packaging expectations
If some details are still evolving, early discussion often helps refine the manufacturing approach before pricing is finalized.
What usually influences the cost of CNC turned parts?
Cost is most often driven by how efficiently a part can be produced and repeated. Common drivers include:
- Setup complexity and number of required operations
- Tight tolerances or surface finish requirements across many features
- Material behavior, chip control, and tooling wear
- Cycle time impacted by milling, drilling, or back-working
- Release sizes that repeat setup effort too frequently
Looking at functional requirements early can identify cost-reduction opportunities without compromising performance.
How do manufacturers maintain consistency across repeat CNC turning releases?
Long-term consistency comes from disciplined process control, not just first-article qualification. That generally includes standardized workholding, documented tooling and offsets, in-process checks on critical features, and inspection routines tied to print requirements.
Once a turning process is validated, those controls keep parts consistent across future releases—even months or years later.
In what situations should CNC turning in Manchester, NH, be combined with milling or other operations?
Many production components start with turning for core geometry and then use milling or other processes for additional features.
This approach works well when flats, slots, cross-holes, or interfaces must stay aligned to turned features, or when completing everything in one workflow reduces handling and setup variation.
When is the right time to involve a machining partner in a CNC turning project?
Involving a machining partner early creates more opportunity to optimize the process before cost, lead time, or repeatability concerns are locked in.
- Material and stock selection
- Tolerance strategy on functional features
- Setup count and operation sequencing
- Whether parts can be completed in a single workflow
When prints are still evolving, early discussions often help prevent unnecessary changes later.
Can Manchester, NH, CNC turning support both low-volume and long-term production programs?
CNC turning frequently supports early production, bridge quantities, and long-term repeat programs.
The difference isn’t volume—it’s whether tooling, workholding, and inspection plans are built with future releases in mind. When those elements are in place, the same turning process can scale without needing to be rebuilt later.
What part does inspection play in Manchester, NH, CNC turning for repeat production?
Inspection validates that the turning process is maintaining critical features, not simply achieving a one-time pass.
- Critical diameters, bores, and threads
- Relationships between concentric features
- Consistency across lots and releases
The focus is long-term confidence and stability, not inspecting every dimension on every part.
How repeat releases compare to continuous production runs?
Repeat releases introduce time gaps, which makes process discipline more important than raw speed.
- Documented setups and tooling
- Controlled offsets and tool life
- Clear inspection benchmarks
Those controls support restarting production months or years later while maintaining the original intent.
How does production-ready Manchester, NH, CNC turning differ from job-shop turning?
The distinction isn’t the machine itself, but the mindset behind how the process is run.
Instead of focusing on one-off orders, production-ready turning emphasizes stability, documentation, and repeatability across releases. That mindset shows up in programming, workholding, inspection strategy, and scheduling discipline.
Why Choose Roberson Machine Company for Manchester, NH, CNC Turning?
Process control, equipment, and production experience come together at Roberson Machine Company to support reliable, repeatable CNC turning. Long-term production cycles are supported through stable workflows and tooling strategies built to keep releases on schedule.
When CNC turning progresses past prototypes into repeat production, execution matters more than raw capability. Keeping parts consistent and programs on track requires process control, setup discipline, and production experience. Roberson Machine Company is built around:
- Turning workflows engineered to maintain critical diameters, bores, and sealing features across repeat releases
- One-setup machining strategies that reduce handoffs, cycle time, and alignment risk
- Process control that supports consistent parts from first article through long-run production
- Material experience across stainless, aluminum, alloys, titanium, and production-grade polymers
- Scheduling discipline and tooling strategies designed to minimize scrap, delays, and downstream variation
Additional CNC services available include:
- CNC Lathe Machining
- Custom CNC Machining for Part Production
- CNC Machine Automation
- Oil and Gas Precision Machining
- Aerospace Manufacturing
- Automotive Part Manufacturing
- EDM Machining
- High Volume CNC Machining
- Industrial Automation
- Solar Panel Manufacturers
Roberson Machine Company supports new releases, scaled production, and ongoing CNC turning programs built for consistency and long-term reliability. Learn more about our team and capabilities, request a quote online, or call 573-646-3996 to review your Manchester, NH, CNC Turning project, timelines, and requirements.


